With the establishment of the Kyoto Protocol in December 1997, greenhouse gas reduction targets for the prevention of global warming were clarified and the spotlight was placed on the issue of generating and absorbing carbon dioxide. In response to these developments, Yamaha started to tackle research in mechanical engineering in an effort to improve the fuel efficiency of its motorcycle and automobile engines, which are a source of CO2. The company also expanded its horizon and began research in biotechnology based on the idea that CO2 could be used as a resource. Yamaha particularly focused on the exceptional photosynthesis capacities of microalgae and began to develop technology for the absorption and fixation of CO2 using photosynthesis (creation of oxygen and organic matter from CO2 and water using sunlight).

In 2000, Yamaha had been working to develop a photobioreactor that would conduct photosynthesis using sunlight. The technology caught the eye of Nisshin Oil Mills, Ltd. (now Nisshin Oillio Group, Ltd.), and research on the mass culturing of Chaetoceros was accelerated. Chaetoceros is a single-cell floating algae phytoplankton used as a food source during the larval stage of shellfish (giant oysters, pearl oysters, clams, etc.), echinoderms (sea cucumbers, sea urchins, etc.) and crustaceans (shrimp, crab, etc.), but it is quite difficult to stably culture.

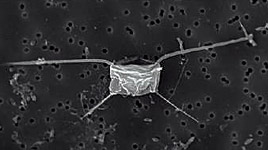
However, in February 2002, Yamaha and Nisshin Oillio succeeded in efficiently culturing Chaetoceros on a mass scale by increasing its density approximately six times compared to existing culturing technologies. Production of Chaetoceros began at Yamaha in December 2003, while sales were handled by Nisshin Marine Tech Co., Ltd., a marine feed manufacturing subsidiary of Nisshin Oillio.
In addition, with a view to expanding the Chaetoceros business, Yamaha constructed a new business compound with cutting-edge facilities in Fukuroi, Shizuoka Prefecture in 2005. Along with initiatives to reduce CO2, Yamaha sought to establish areas of business that were beneficial to society and pursue their potential by focusing on the development of technology and devices to recycle CO2 as a resource.
.










