- 日本語
- English
- Bahasa indonesia
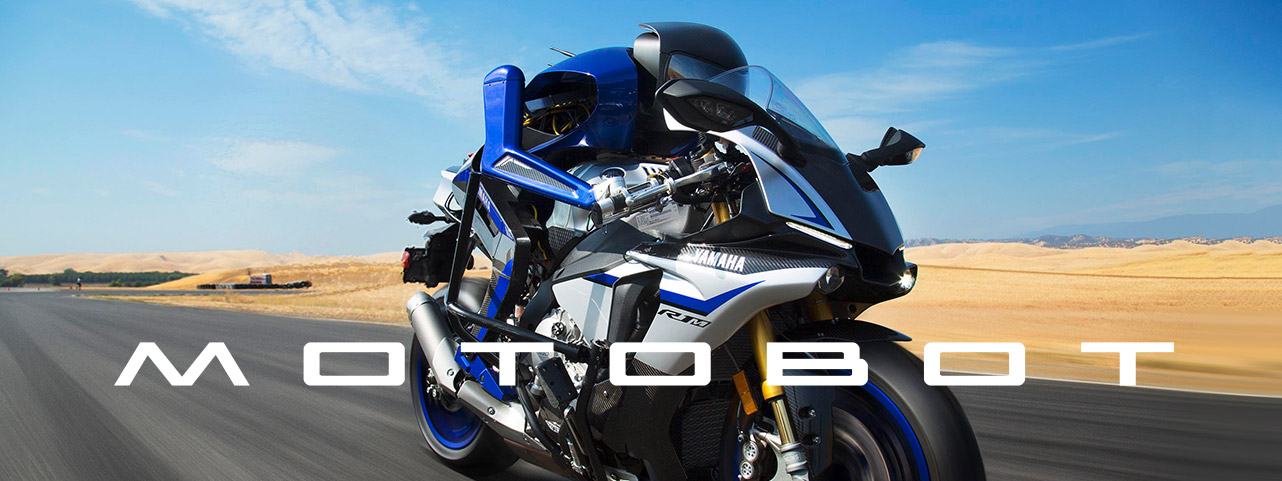
What is MOTOBOT ?
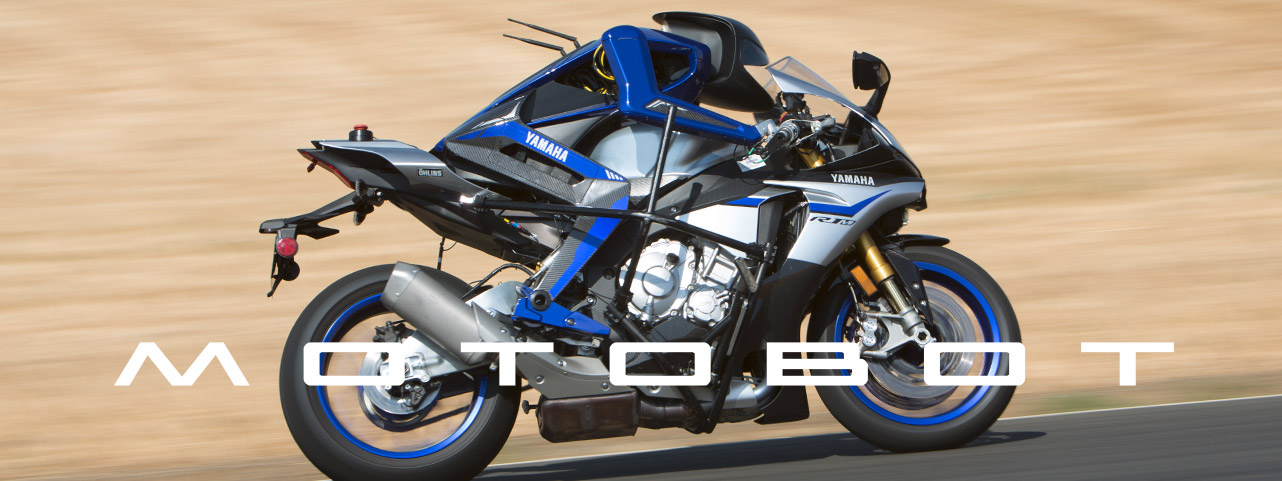
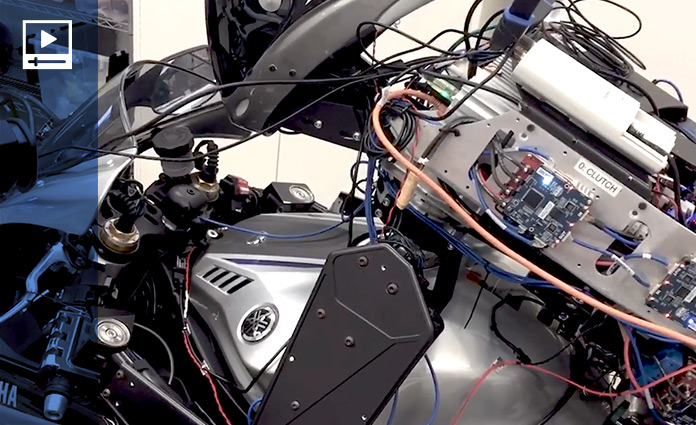
What makes the MOTOBOT project unique is its approach to completely automated operation. Unlike the current methods used for automobile self-driving systems, which have progressed in recent years, the aim is for a humanoid robot to operate a vehicle unmodified for autonomous use. Based on data for vehicle speed, engine rpm, machine attitude, etc., MOTOBOT will control its six actuators* to autonomously operate the vehicle. Going forward, technology for machine position recognition (high-precision GPS, various sensors, etc.) and machine learning will be utilized to enable MOTOBOT to make its own decisions regarding the best lines to take around a racetrack and the limits of the motorcycle’s performance, so that it can improve its lap times with successive laps of the track. From this project, we will be able to visualize data about human motorcycle operation, deduce the relationship between rider input and machine behavior, and then use the resulting know-how in developing vehicles for creating even greater Kando. Also, by altering MOTOBOT’s control programming and the shapes of its operating mechanisms as necessary, we anticipate it will also be adaptable to ride other vehicles like personal watercraft and snowmobiles.
* For operating the steering, throttle, front brake, rear brake, clutch and gearshift pedal
MOTOBOT Technologies
The Future Possibilities MOTOBOT Will Create
By using MOTOBOT technologies to optimize control of vehicle dynamics,
we will develop higher performing and safer forms of mobility.
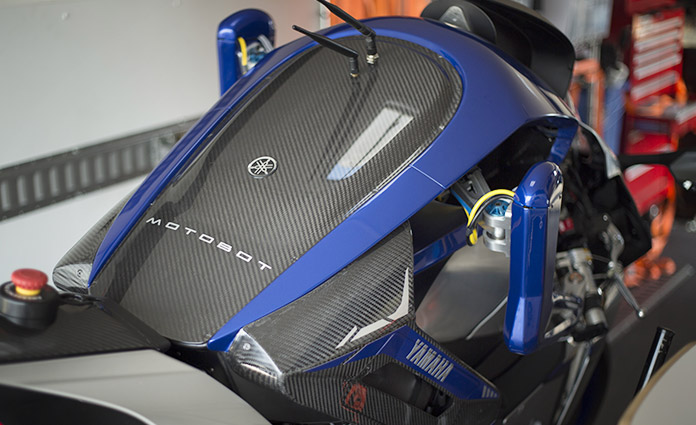

MOTOBOT fuses Yamaha Motor's technology gained from developing motorcycles (vehicle dynamics know-how, electronic control, etc.) with technology garnered from developing our industrial robots (robot control, etc.).
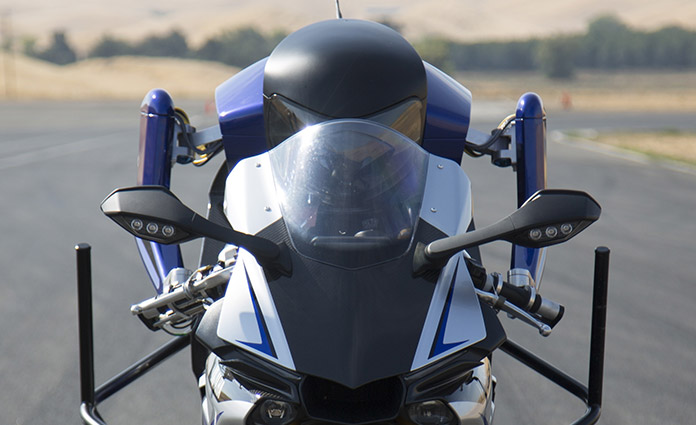

The various actuators that perform riding operations are precisely controlled and can perform actions similar to a human rider.
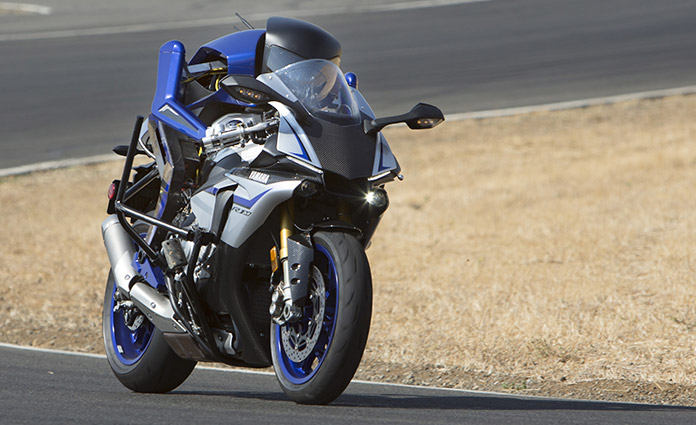

Improving the algorithms for operating the mechanisms required for high-speed track riding and other enhancements will eventually lead toward making other types of high-level riding techniques possible.
Roadmap

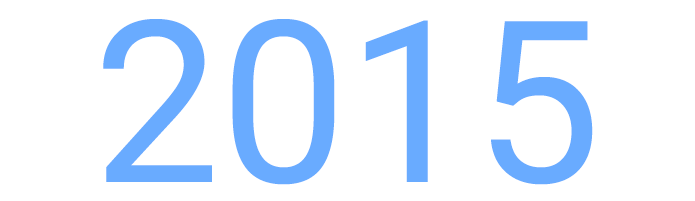
Aims: Straight-line riding up to a top speed of 100 km/h; running a slalom course; cornering


Aims: Deduce the requirements for riding that exceeds human capabilities; lap a racetrack at 200 km/h or higher


Aims: Use the underlying technologies obtained through developing MOTOBOT, such as robot control and human-machine interface creation, as a basepoint for continuing R&D towards creating new value.
Open Innovation
MOTOBOT is an open innovation project and development is moving forward in partnership with world-leading research institute SRI International in order to clear the unique and high goals presented by the project.