| Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. (YMC) announces
the debut of the new remake of the Yamaha Sports “YZF-R1”
in its 2004 European market model at the 60th Milano
Show (bicycles and motorcycles) opening on September
16 2003.
After its debut at the Milan show in September of 1997
(as a 1998 model), the original YZF-R1 quickly won unprecedented
acclaim as a model that offers “full enjoyment
riding a 1000cc machine” and also as “the
super cornering machine” instantly set a new standard
for the supersport category. Since then, with its first
minor model change in 2000 and a further evolution in
2002 that added a new frame and fuel injection among
other features, the YZF-R1 has continued to lead the
supersport market.
The new 2004 YZF-R1 maintains the same model concept
that has held consistent from the first-generation (1998),
second (2000) and third-generation (2002) models while
adding the latest Yamaha technologies to achieve an
outstanding balance of (1) styling, (2) performance
and (3) the kind of agile cornering performance to make
it a “beautiful, exciting sports machine that wins
the title of fastest in secondary road riding.”
The result is a model that takes the 1000cc supersport
category into an entirely new dimension.
 |
2004
European market model Yamaha Sports “YZF-R1” |
|
Name: |
Yamaha “YZF-R1” |
Release: |
February 2004
(Date to vary with the different European distributors)
|
Coloring:
|
Deep Red Metallic K
Deep Purplish Blue Metallic C
Dark Bluish Gray Metallic 8 |
|
 |
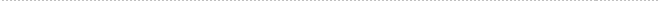 |
| Market Background
and Product Summary |
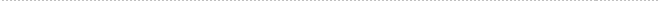 |
 |
Demand in the European supersport market
has held steady in recent years at an annual level of
150,000 units. This market can be divided roughly into
the 600cc class and the over 750cc class. This over
750cc class (= 1000cc models) has been the center of
increasing attention since the change in the World Superbike
regulations that allows entry of 4-cylinder 1000cc models
beginning with the 2003 season.
To this 1000cc class, the various makers have introduced
many new models, but the Yamaha YZF-R1, as it has continued
to mature from the first-generation model through the
second (2000) and third-generation (2002) models, continues
to maintain strong user following and influential position
as a symbol of the 1000cc supersport bike. The reasons
that most people give for this continued popularity
is the R1’s innovative styling and its great cornering
performance.
Meanwhile, user needs have continued to diversify in
recent years with different customer groups looking
for (1) performance and function, (2) utility and (3)
styling.
Considering these customer trends, the product concept
for the new YZF-R1 was to further develop the existing
model’s already outstanding cornering capabilities
while adding a new dimension of performance to make
this an exciting new supersport model. The development
concept was defined as a “beautiful, exciting sports
machine that wins the title of fastest in secondary
road riding.” By adopting design ideas from the
MotoGP machine YZR-M1 and the latest technologies available
throughout the design the idea was to build a model
that had a great balance of the three elements of “cornering,”
“performance” and “styling.” The
result is a machine character defined by,“unmatched
power in secondary road riding and the performance to
let you handle it at will.” |
 |
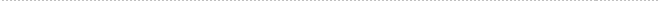 |
| Main Features
|
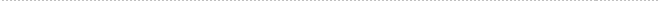 |
 |
 |
Engine |
|
1) New-design big bore, lightweight
engine
In order to achieve high-level performance and cornering
potential, the new YZF-R1 adopts a newly designed power
unit. The heart of this unit is the liquid-cooled, 4-stroke
DOHC, 40-degree forward-inclined, in-line-4-cylinder,
5-valve, fuel injection-equipped engine designed especially
with optimum intake-exhaust efficiency in mind.
Compared to the existing YZF-R1’s this new engine
has been bored out another 3mm and given a bore x stroke
of 77.0 x 53.6mm (74.0 x 58.0 for existing model), optimized
throat diameter, a new compact combustion chamber, forged
aluminum pistons, high-lift cams and a high compression
ratio of 12.3 : 1, from which its delivers a maximum
power output of 172 PS/12,500 rpm (when not including
forced-air intake). Furthermore, thorough weight reducing
measures throughout the engine have made it approximately
4 kg lighter (engine alone). In combination with the
close-ratio 6-speed transmission, this delivers performance
truly worthy of being called “No.1 in Performance.”
2) Closed deck type cylinder for higher compression
ratio
In order to achieve a higher compression ratio and power
output, a closed deck type cylinder is adopted. By casting
the cylinder block with a unique Yamaha low-pressure
aluminum casting method to ensure maximum metallurgic
strength, it was possible to make a highly effective
closed deck type cylinder characterized by the fact
that the coolant passages do not go through the head
portion, thus enabling a more rigid structure. Ensures
excellent reliability to accommodate the high compression
ratio, high output cylinder. And, thanks to design efforts
to reduce the cylinder pitch as much as possible, the
lateral width of the cylinder is only 4mm wider than
the existing model despite the increased bore.
Furthermore, a direct plated liner-less cylinder (ceramic
composite plating) format has been adopted to ensure
outstanding heat dissipation characteristics, improved
rigidity balance and the capacity for a more accurate
cylinder shape.
3) FS conrods adopted for outstanding reliability
To ensure conrod reliability in light of the increased
power output, so-called FS conrods (Fracture Splitting
Connecting Rod) are adopted for the large end of the
connecting rods for the first time ever on a Yamaha
motorcycle (machined conrods have been used until now).
In this method, the large end of the rod is machined
into a cylindrical shape and then shock-split. When
assembling, the matching split surfaces are rejoined
and bolted together to form a highly precise cylindrical
form again which contributes to outstanding reliability
in high-rpm use. (FS conrods = Fracture Splitting Connecting
Rods)
4) Fuel injection and sub-throttle for ease of use
in low- to mid-speed range
In order to obtain outstanding performance while also
improving the engine’s environment-friendliness,
this model adopts a fuel injection (FI) system. The
injector is a highly reliable plate type, long nozzle
unit with two-direction, four-outlet design for outstanding
dynamics range.
And, what makes the YZF-R1 system unique is the adoption
of a motor-operated sub-throttle valve controlled on
the basis of information about engine rpm and the throttle
opening fed back via the ECU in order to provide excellent
power control characteristics. The functioning of the
main and sub throttle valves enables optimum control
of the intake air flow speed. This enables optimized
volume efficiency across the entire rpm range, thus
resulting in the kind of outstanding low- to mid-speed
drivability only digital control can provide.
A link mechanism has also been added to the butterfly
action in order to achieve a more compact design that
results in a throttle body that is 27mm slimmer in lateral
width than the existing YZF-R1. This slimmer throttle
body has in turn allowed greater freedom in the design
of the new high-rigidity frame that contributes to this
model's outstanding handling characteristics.
5) Air induction contributes to excellent response
characteristics
An air induction system is adopted to increase intake
efficiency by utilizing the natural air flow during
riding to pressurize the air in the air box. In this
system, two intake ducts located below the headlights
channel air to the dirty side of the air cleaner positioned
in front of the fuel tank. From there it passes through
the filter and is then pressurized on the large-capacity
clean side. The induction and pressurizing of this cool
air supply is an important factor in improving power
development and giving the new YZF-R1 its outstanding
response during acceleration.
6) Compact design EXUP connecting two cylinders each
Yamaha’s EXUP system that functions to eliminate
torque valleys and provide excellent power development
characteristics has been made more compact on this model
while retaining the same basic operating principle.
Unlike the former system that included a separate valve
for each of the four exhaust pipes, the system on the
new YZF-R1 places just two EXUP valves at the points
where the four exhaust pipes merge into two, thus creating
a more compact system that controls the pulse based
on calculations of the 1st and 2nd cylinders’ exhaust
and the 3rd and 4th cylinders’ exhaust. The material
used in the new valves has also been changed, from SUS
to titanium. With the bodies also made of titanium,
this now makes them all-titanium units.
7) Up-muffler design for excellent exhaust efficiency
and distinctive look
An up-slanting muffler has been adopted that gives a
highly impressive look to the exterior. The exhaust
system is designed with optimum pipe lengths, silencer
expansion chamber and sizes of the different pipes so
as not only to bring out the performance of the new
engine in the most efficient way but also to create
a boldly impressive accent to the machine’s styling.
8) Other engine-related features
Other features include (1) a forged aluminum retainer
to accommodate the higher revving engine, (2) an optimized
flywheel mass setting (20% lower than the existing YZF-R1)
that provides thrilling acceleration feeling, (3) a
round type radiator for excellent cooling performance
and (4) an ACM (Alternating Current Magneto) positioned
at the rear surface of the crankcase to ensure a deep
banking angle and a low engine center of gravity. |
 |
Chassis |
|
1) New Deltabox V (Victory) frame
with 2.5 times greater rigidity
The new YZF-R1 adopts a newly designed frame we call
the Deltabox V (Victory). Incorporating design aspects
of the frame of our YZR-M1 and 3D CAD analysis, this
new frame has been given a high level of rigidity to
make it fully viable for circuit riding and stock class
racing. With this aim in mind, the main frame was designed
narrow in the lateral direction and the head pipe and
pivot connected more directly in a straight line.
For the outside portions of the main frame high-elasticity
panel stock has been used, while high-strength cast
parts are used for the inside and the two welded together
to create box sections for a highly reliable hollow-type
frame structure. Also, the use of optimum types of aluminum
stock in the various parts, like cast parts for the
pivot assembly, and the right thickness of stock have
contributed to the good overall rigidity balance. As
a result, the rigidity values compared to the existing
YZF-R1 have been increased 2.5 times for longitudinal
rigidity and 1.3 times for lateral and torsion rigidity.
2) Optimized engine mounting position and weight
distribution for excellent initial-stage steering characteristics
In order to achieve high-level steering performance,
especially in the initial stage, the engine mounting
position, front-rear weight balance and cylinder forward
incline angle (angle increased from 35 to 40 degrees)
have been optimized in relation to each other in terms
of position and balance. Compared to the existing model
the engine center of gravity has been lowered and moved
toward the front wheel. This combines with the effect
of optimized dimensions like a 5mm increase in the fork
offset to 30mm to help achieve stable handling that
lets the rider enjoy quicker response characteristics
in initial-stage steering action.
3) High-performance front and rear suspensions and
rear arm with upside-down truss configuration
In the front suspension, the upside-down fork with 43mm
diameter tubes provides both excellent cushioning and
quick handling characteristics. And, the rear liked-type
suspension adopts an aluminum rear arm with an upside-down
truss configuration to balance the positioning with
the new up-muffler. This provides excellent rigidity
balance and cushioning performance. Also, the rear suspension’s
preload adjuster is now made of aluminum for added quality
look. The rear frame is constructed of parts made by
Yamaha’s CF aluminum die-cast method that boosts
welding characteristics and aluminum sheet metal to
create a box structure that gives greater rigidity while
also contributing to a higher quality aluminum look
to the exterior.
4) Front brake with radial-mount caliper
A new brake system has been developed to match the machine’s
increased performance dynamics and provide outstanding
functionality and control characteristics. The front
brake features a 320mm diameter disc and radial type
pump that enables a larger lever action for the master
cylinder and excellent control characteristics. The
caliper is given a radial mount that minimizes distortion
induced by the reactive force during braking. These
factors combine to help ensure stable braking power
and control especially during hard braking. This radial
type mount is also characterized by excellent response
during brake release that enables well-modulated braking
action. The rear brake adopts a 220mm diameter disc
for excellent braking function and control characteristics.
5) Fuel tank with separate cleaner and tank sections
Replacing the old design where the fuel tank enveloped
the air cleaner box, the new design is characterized
by the fact that the cleaner is moved forward and completely
separated from the new slimmer tank (50mm slimmer in
left-right width than the existing model). Combining
with the slimmer frame design, this gives excellent
knee grip characteristics.
Also, while the seat is thinner at the tank end, in
the middle portion, which is the critical part during
weight shifting, a sufficient surface area has been
provided to ensure good machine hold for the rider.
The handlebar and footrest position have also been changed
to match the new engine character.
6) Bold new 2-facet body design
The body design of the new YZF-R1 is defined by new
front view and rear view, each of which features a 2-facet
design. With its new 4-lamp headlight design, the front
view has an expression that exudes pure power. At the
same time, the air ducts are designed to give the impression
of drawing in large volumes of air. On the other hand,
here are also lines that stress sleek aerodynamics,
expressed in the sense of flow of the air from the leading
edge of the upper cowl smoothly back along the body
and directly into the intake.
As for the tail assembly, the up-muffler gives an expression
of performance, while the combination of the muffler
and the tail cowl in their integrated design also express
aerodynamics. Meanwhile, the muffler itself is designed
to create an image of the power flow from intake to
combustion and exhaust. What's more, the compactness
of the muffler layout helps give an impression of the
flow of air around the tail that is a new accent point
of the YZF-R1.
7) Other Features
Other features include (1) new lightweight 5-spoke wheels
with optimized rigidity balance between the hubs and
rims, (2) new-design meter panel with the tachometer
to the center (a liquid-crystal speedometer and clock
on the left and the liquid-crystal tripmeter on the
right), (3) a two-lamp, 4-bulb headlight design and
super-lightweight cowling that accentuate the renewed
styling of the YZF-R1, (4) LED tail lamp and (5) a single-unit
lightweight die-cast rear frame designed to match the
up-muffler layout. |
 |
 |
| 2004 European
Model Yamaha “YZF-R1” Technical Specification |
 |
 |
Overall
length x width x height
Seat height
Wheelbase
Dry weight
Engine type
Cylinder arrangement
Displacement
Bore x Stroke
Compression ratio
Maximum power
Maximum torque
Starting system
Fuel tank capacity
Fuel supply system
Tire size (Front / Rear) |
2,065mm
x 720mm x 1,105mm
835mm
1,395mm
172kg
Liquid-cooled, 4-stroke, DOHC, 5-valve
In-line 4 cylinder
998 cc
77.0mm x 53.6mm
12.3 : 1
126.4kW(172.0PS) / 12,500rpm (without direct air
induction)
106.6N-m(10.9 kgf-m) / 10,500rpm (without direct
air induction)
Electric
18liters
Electronic control fuel injection
120/70ZR-17 / 190/50ZR-17 |
|

|