Multi-cylinder Engines
Revs Your Heart – Explore the world of Yamaha motorcycles
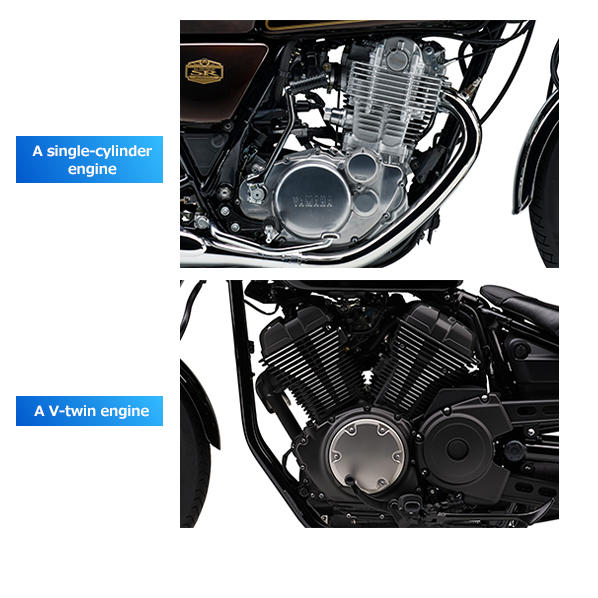
Why a Single-cylinder Isn't Right for High Output?
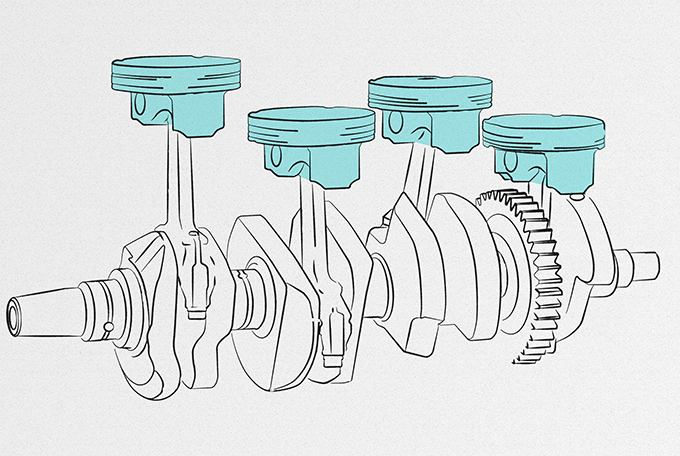
The desire for greater power output in motorcycles has led to engines with larger displacement and multiple cylinders, but why exactly is there a need for more cylinders? Why can’t you just increase displacement using one cylinder with a larger bore and combustion chamber? The fact is that a combustion chamber with an inner diameter of about 10 cm is the practical limit for a gasoline engine. Since the combustion process begins from the place closest to the spark plug, it takes a certain amount of time for the entirety of the air-fuel charge in the chamber to combust. The larger volume of the combustion chamber, the longer full combustion takes, which makes the engine less practical for motorcycle use. That is why multi-cylinder engines have become the standard method to create large-displacement, high-power models.
Furthermore, multi-cylinder motorcycle engines come in a variety of formats to best fit each model’s concept, ranging from in-line 2- 3- and 4-cylinder engines to V-twin and V4 engines. With in-line multi-cylinder engines, the more cylinders there are, the wider the engine becomes, although design efforts in recent years have helped make them more compact. However, with longitudinally mounted multi-cylinder V-type engines, the engine is inherently slimmer in terms of width, thus allowing a slimmer body design. It is these various types of multi-cylinder engines that have enabled the higher displacement not possible with a single cylinder.