Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. has recently succeeded in the development of a new-generation "SD (Super Diesel) Engine," a project that has been in progress for some years with the aim of creating an engine for automobiles that answers the environmental needs of the 21st century. This is a compact, environment-friendly engine characterized by low fuel consumption and low emissions capable of running 100 km on about 3 liters of fuel while also meeting the proposed Euro4* emissions.
This newly developed engine has been given the name SD (Super Diesel) and is a 1000 cc displacement engine combining a "2-stroke diesel " format and a Yamaha-exclusive combustion system. It includes a number of qualities that make it excellent as a power unit for environment-friendly compact cars. |
 |
 |
 |
Main features of the 1000 cc SD (Super Diesel) Engine |
 |
 |
1) Toxic exhaust emissions have been reduced to the proposed Euro4 levels (roughly 50% lower than the current Euro2 standards for CO and 60% lower for Hydrocarbons (HC) + Nitrogen oxides (NOx) and 70% lower for particulate matter.
2) A comprehensive engine control system greatly reduces the typical diesel engine exhaust characteristics such as black smoke.
3) Realization of 3-liter car (a car capable of running 100 km on 3 liters of fuel) level fuel economy.
4) Realization of high response, high torque and high power output (roughly 50% increase in torque in low to middle rpm range and 30% increase in max. power output when compared with a conventional diesel engine of the same class without supercharging)
5) Realization of light weight and compactness (30% reduction in volume, 20% reduction in weight compared with a conventional diesel engine of the same power output without supercharging) offers greater freedom of design for use in compact cars and the potential to improve overall performance as an automobile by contributing to basic performance and drivability.
6) Durability and reliability sufficient to pass the various types of tests such as 250-hours max. power output tests.
* What is "Euro4": At present Europe administers the Euro2 emissions standards. The stricter Euro3 standards are scheduled to be adopted in the year 2000 and plans are now being made for Euro4 standards to be adopted in 2005. The values to be adopted in this 4th standard (see item (1) above) are still at the proposal level. |
 |
 |
Main Effects |
 |
 |
During the development stage primary concern was placed on combining the lightness, compactness and powerfulness inherent in a 2-stroke engine with the inherently low fuel consumption and low CO2 emissions of a diesel engine to the highest degree possible. In this way we achieved high power output without the use of a supercharger and at the same time environment-friendly low emissions values were realized. Furthermore, the relative simplicity of the structure gave this engine additional merits in the areas like ease of mainte nance and lower manufacturing cost.
What's more, we have used the following advanced Yamaha small-engine technologies and other technologies gained over many years of research and development activities to solve the weak points usually associated with 2-stroke engines and diesel engines, including durability, NOx emissions and smoky exhaust. |
 |
Big reduction in NOx emissions |
|
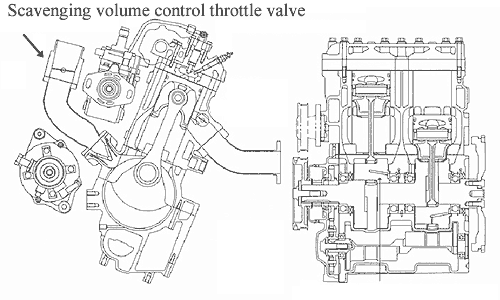
By attaching a scavenging volume control throttle valve to the intake manifold, which is controlled electronically, it is possible to control the amount of residual gas in the cylinder, thus optimizing combustion in a way that greatly reduced NOx emissions. |
 |
Diesel-inherent black smoke reduced to level where it is no longer visible |
|
In the sub-combustion chamber a multiple nozzle injector adopted, while the main combustion chamber is a unique new design that utilizes four connecting jet passages from the sub-combustion chamber to achieve high combustion efficiency. Furthermore, a comprehensive engine control system is employed that greatly reduces both the black smoke typical with a diesel engine, thanks to an electronically controlled injection pump and the white smoke typical of a 2-stroke engine, thanks to oil-supply control, to levels that cannot be detected by the naked eye. |
 |
High durability, reliability achieved |
|
Electronic control of lubrication oil supply by the engine control system makes it possible to reduce oil consumption to an absolute minimum, while at the same time a new oil distribution system has been adopted that supplies asufficient amount of oil specifically to the points where it is needed: the crank journal bearing, the large-ended needle bearing and sprayed directly on the walls of the cylinder.
Furthermore, superior levels of durability and reliability have been achieved through the adoption of heat-resistant lubrication oil and a full range of Yamaha engine design know-how in features like a piston and piston rings highly resistant to heat deformation and Ni-P-SiC-plated cylinders also designed with consideration to heat-deformation resistance.
This new SD engine was also designed with consideration for its potential use as the base for a hybrid engine, thus making it Yamaha's offering for a truly new-generation engine for the 21st century. Of course, it will be possible to utilize this new engine's technology on a technical-assistance or OEM supply basis with both domestic and overseas automobile manufacturers.
At Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. we believe that "our lives are dependent on the irreplaceable resources of the earth and the natural environment" and in line with our corporate mission of creating "Kando -- Touching People's Hearts,"
we are always concerned with achieving a "balance between the environment and Kando" and pursuing corporate business activities that are environment-friendly.
In our quest to create products that are friendly to nature and the environment, Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. has achieved such milestones as the development and sales of the world's first electro-hybrid bicycle, Yamaha PAS (1993) and the development of a new "2-stroke motorcycle engine exhaust cleaning system" (1999).The development of this new automobile SD engine is yet another of Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.'s environment oriented projects. |
 |
 |
Technological Features |
 |
 |
 |
1) Yamaha-original combustion system with four connecting jet passages achieving high power output, low fuel consumption and low emissions |
|
The injector nozzle is located in the sub-combustion chamber which is connected to the main combustion chamber by means of four connecting jet passages in a unique new Yamaha design. The four jet passages are shaped in a way that helps generate a swirl as the fuel/air mixture enters the combustion chamber, while their shape is also optimized to offer the minimum of resistance to the flow of the ignition flame into the main chamber from the sub-combustion chamber. In this way, the design has been able to achieve both a strong swirl effect and a reduction in "throttle loss," thus contributing to outstanding combustion efficiency that helps achieve high power output, low fuel consumption and low emissions. |
 |
 |
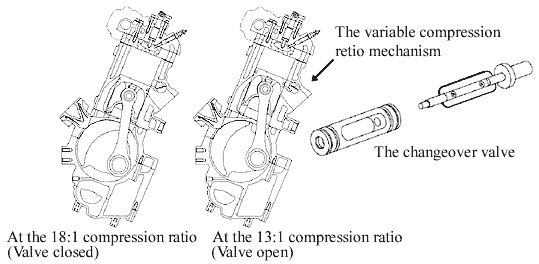
2) Variable compression ratio system boosts low- to mid-speed torque while maintaining high power output |
|
This engine adopts a variable compression ratio mechanism that adjusts the compression ratio in accordance with the engine rpm and load. This system adopts a Schnurle type 2-stroke structure with scavenger that makes it relatively easy to vary the compression ratio by changing the distance from the location of the piston dead top center and the exhaust port. To this an exhaust port with upper and lower stages is adopted along with a changeover valve located in the upper port which can be opened and closed to change the compression ratio over a 13~18 : 1 range.
Controlling the ratio so that the higher ratio is used in the low-to mid-speed range and the lower ratio in the high-speed range with medium load or over in order to achieve both smooth torque development and a high power output of 33kW/liter, unprecedented until now in a diesel engine without a supercharger. In particular, there is a roughly 50% increase in torque in the low to middle speed range compared to a conventional diesel of the same displacement. |
 |
 |
3) Big reduction in NOx emissions with scavenging volume control throttle valve |
|
The adoption of an electronically controlled scavenging volume control throttle valve to the intake manifold that can be opened and closed in accordance with engine load and rpm makes it possible to decrease the amount of intake air and increase the residual gas in the cylinder, especially when running with low engine load, by closing down the throttle valve. This serves to keep the combustion chamber temperature lower and reduce the concentration of oxygen, which in turn reduces the oxidation of nitrogen in the combustion chamber to a minimum and reducing the amount of NOx produced. |
 |
 |
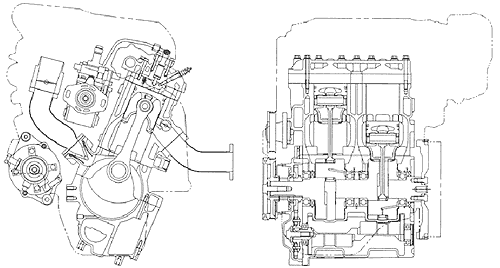
4) Compact design reduces weight 20% and volume 30% |
|
Because this is a 2-stroke engine there is no need for valve drive mechanisms or an oil tank, thus enabling a more compact design. Also, by optimizing the combustion pressure we were able to rationalize the design in a way that minimize the load on engine's strength-member materials. As a result, a weight reduction of about 20% and volume reduction of about 30% was achieved incomparison to a conventional diesel engine of the same power output. In particular, it was possible to achieve a big reduction in size in areas like the height of the cylinder head, thus affording greater design freedom when mounting this engine on a compact car. |
 |
 |
5) Engine control system |
|
The adoption of an engine control system that controls the various functionsof the engine like the fuel injection system, the lubrication system, the variable compression ratio system and the scavenging volume control throttle valve in accordance with running conditions, provides comprehensive support in helping the SD engine achieve its superior power output, low fuel consumption and low emissions, as well as its high degree of durability and reliability. |
 |
 |
Specifications of the Yamaha SD (Super Diesel) Engine |
 |
 |
Engine format |
2-stroke diesel |
Cylinder layout |
In-line twin |
Displacement |
982 cc |
Bore x stroke |
82 x 93 mm |
Overall length x width x height |
374 x 565 x 550 mm |
Weight |
95 kg |
Fuel consumption (EU Mode) |
3-liter/100 km |
Max. power output |
33kW/4000 rpm |
Max. torque |
80Nm/2500 rpm |
Emissions standard met |
Euro4 proposed levels |
|