New technology
Introduction to the new technology of our Multi Purpose Engine.
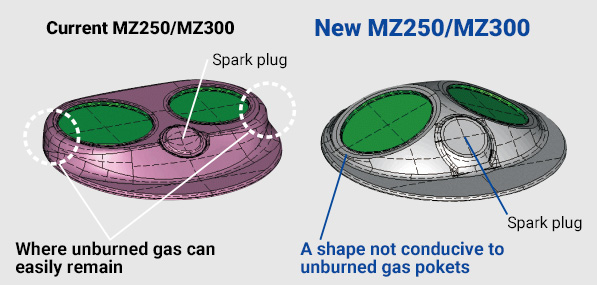
Hemispherical combustion chamber
A fast combustion speed is necessary to increase combustion efficiency. Since the compact size and shape of the hemispherical combustion chamber adopted on MZ250/MZ300 reduces the distance that the combustion flame ignited by the spark plug must travel, less gas remains unburned and the combustion speed is increased. This results in improved fuel efficiency.

DIFFERENCE IN COMBUSTION CHAMBER SHAPE
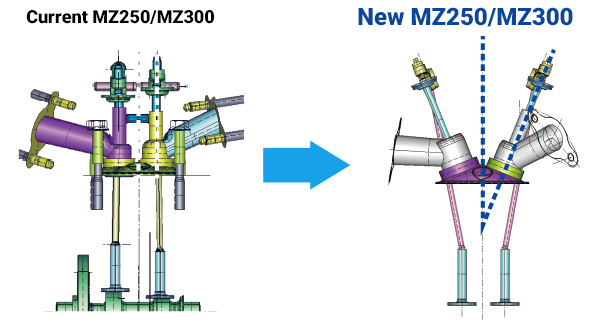
Valve angle
To enable a hemispherical combustion chamber shape, the intake and exhaust valves were set at an angle of 22°. To accommodate this angle, the intake port shape was also changed. The interior of the combustion chamber is conducive to creating a swirl that speeds up combustion, boosts combustion efficiency and helps achieve better fuel efficiency.
Ignition timing
Since the hemispherical combustion chamber increases combustion speed compared to the current engine, the ignition timing (advance) has also been changed from the current model's BTDC23° to the new model's BTDC20°. This made it possible to clear the emissions standard requirements.
Explanation: Ignition timing (or ignition advance) means the timing of the firing of the spark plug. It is expressed in terms of the number of degrees of [crank] angle before the piston reaches top dead center in its compression stroke that the ignition is set to fire at. For example, BTDC25° (BTDC = Before Top Dead Center) would mean that the ignition fires at the point where the crank angle is 25° before top dead center, which is designated as 0°. The reason for such an advance in the timing of the ignition is because it would take some time for the ignition flame to spread through the air-fuel mixture in the entire combustion chamber if the ignition was fired when the piston reached top dead center.
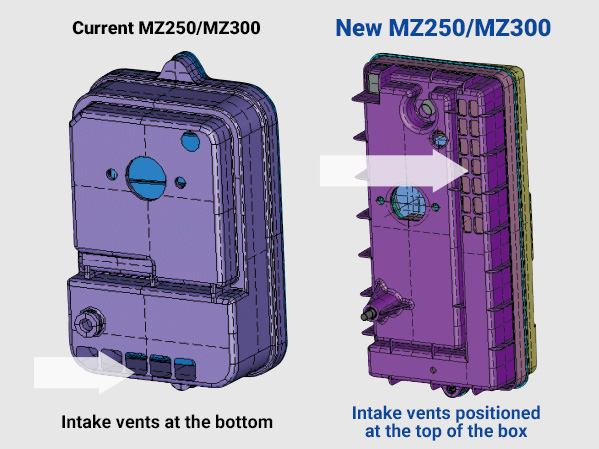
Air cleaner with new air intake position (only on Silent Semi-dry series)
Both the MZ250/MZ300 models have a new air cleaner design with the intake vents located at the top of the box where the intake air is less influenced by engine heat and less likely to draw in dusty air.Also, a new filter material has been chosen to minimize dust intake and improve fuel efficiency and maintenance.
AIR CLEANER DIFFERENCE
Compact design and engineering [MZ300]
Until now, the MZ300 model had been the same size as the MZ360, but now compact design changes throughout the engine have reduced the size of the new model sufficiently to make it the same size as the MZ250.
First of all, the forward incline angle of the cylinder was changed from 28° to 22° from the horizontal to enable a decrease in overall height. At the same time, the shape of the piston and its skirt was changed and the length of the connecting rod shortened (110 mm › 102 mm) for an optimum design that reduced the dimension in the direction of the cylinder head. In addition, a review was made of the head assembly from the standpoint of space efficiency, resulting in a reduction in overall width by setting the breather chamber in the head at an angle.
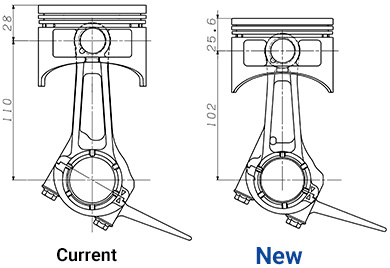
Furthermore, the recoil assembly was made thinner through design changes like positioning a pair of cooling air ducts on two sides, and a thinner air cleaner design was also adopted to contribute to overall compactness. Despite its compact design, the new MZ300 maintains the same level of power output as the current model. As a result, it now has the largest displacement of all the competing models in its size category.*
*As of June, 2012 according to Yamaha Motor surveys
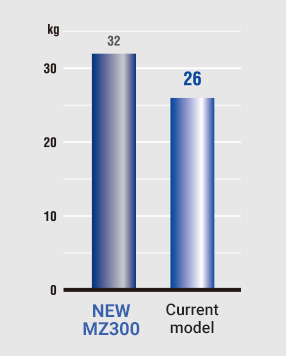
WEIGHT COMPARISON
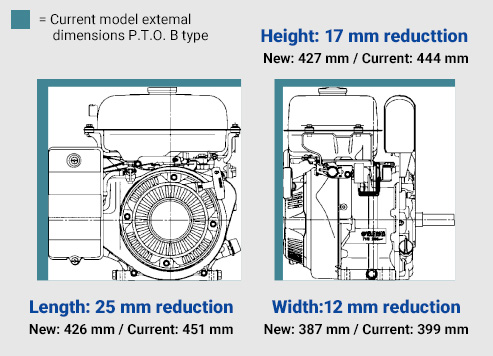
SIZE COMPARISON
Canister Cap for U.S.A. Emission Standard
Chain for prevent from coming off.

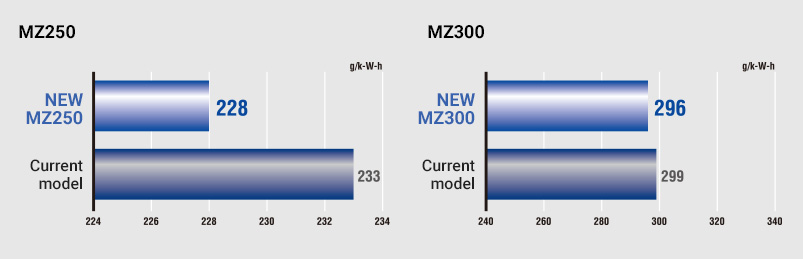
Comparison of fuel consumption per hour